Why Does Weight Loss Cause Diabetes
Weight loss can lead to diabetes due to increased insulin resistance. Excess fat tissue causes hormonal changes.
Weight loss can have a significant impact on diabetes because it can improve insulin sensitivity and reduce the risk of developing the condition. When the body loses excess weight, it can reduce the amount of fat tissue, which in turn can lead to improvements in insulin sensitivity.
This can help the body regulate blood sugar levels more effectively and reduce the risk of developing diabetes. Understanding the connection between weight loss and diabetes can help individuals make informed decisions about their health and take proactive steps to prevent or manage the condition. By maintaining a healthy weight through diet and exercise, individuals can reduce their risk of developing diabetes and improve their overall health and well-being.
The Link Between Weight Loss And Diabetes
The link between weight loss and diabetes is crucial to understand. Insulin resistance plays a significant role in the development of diabetes. When the body becomes resistant to insulin, it leads to elevated blood sugar levels. Rapid weight loss can also impact the body’s insulin sensitivity, potentially leading to the onset of diabetes. It’s important to approach weight loss in a healthy and sustainable manner to minimize the risk of developing diabetes.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/GettyImages-1169212311-181454886e16450b957ed0cdd3967f76.jpg)
Credit: www.verywellhealth.com
Types Of Diabetes Affected By Weight Loss
Weight loss can have an impact on different types of diabetes. For individuals with type 1 diabetes, weight changes may be linked to insulin dosage adjustments. On the other hand, type 2 diabetes is often associated with obesity and weight loss can lead to improved insulin sensitivity and blood sugar control. It’s important to understand the specific effects of weight loss on each type of diabetes in order to manage the condition effectively.
The Science Behind Weight Loss And Blood Sugar Levels
The science behind weight loss and its impact on blood sugar levels is a complex yet fascinating topic. When we lose weight, our body’s glucose metabolism undergoes significant changes. Weight loss affects how our body processes and utilizes glucose, the main source of energy for our cells.
Adipose tissue, commonly known as fat, plays a crucial role in insulin sensitivity. As we shed excess weight, adipose tissue decreases, leading to improved insulin sensitivity. This means our cells become more responsive to insulin, the hormone responsible for regulating blood sugar levels.
By losing weight, we reduce the strain on our pancreas, which produces insulin. With improved insulin sensitivity, our body can effectively utilize glucose, preventing the buildup of excess sugar in the bloodstream. This is particularly important in preventing or managing diabetes.
Understanding the intricate relationship between weight loss, glucose metabolism, and insulin sensitivity is crucial for maintaining optimal health and preventing the onset of diabetes. By adopting healthy lifestyle habits, such as regular exercise and a balanced diet, we can promote weight loss and improve our overall metabolic health.
Unpacking The Weight Loss Paradox
Discover the Weight Loss Paradox and its connection to diabetes. Explore why shedding pounds can lead to this metabolic disorder and gain insights into the underlying mechanisms. Unpack the surprising relationship between weight loss and diabetes in this informative article.
| Unpacking the Weight Loss Paradox |
| Weight loss is often associated with good health, but in some cases, it can trigger diabetes symptoms. This is known as the weight loss paradox. The paradox occurs because when a person loses weight, their body weight set points change, which can affect insulin sensitivity and glucose metabolism. When this happens, the body might become less responsive to insulin, leading to high blood sugar levels and diabetes symptoms. |
| Cases when weight loss might trigger diabetes symptoms |
| One of the cases when weight loss might trigger diabetes symptoms is when a person loses weight rapidly. This is because rapid weight loss can cause a sudden change in the body’s metabolism, leading to insulin resistance and high blood sugar levels. Another case is when a person loses weight but still has excess body fat. In this case, the body might not be able to process glucose effectively, leading to diabetes symptoms. It’s important to note that not everyone who loses weight will develop diabetes, but it’s essential to maintain a healthy weight to reduce the risk of developing the condition. |
The Role Of Diet In Weight Loss-induced Diabetes
Weight loss can increase the risk of diabetes due to nutritional factors. Consuming a balanced diet is crucial in managing this risk.
Exercise: A Double-edged Sword
Exercise is an essential part of a healthy lifestyle, especially for those at risk of developing diabetes. Regular physical activity can improve insulin sensitivity, reduce blood glucose levels, and lower the risk of developing type 2 diabetes. Exercise can also help individuals with diabetes manage their condition by improving blood sugar control and reducing the risk of long-term complications. However, exercise alone may not be enough to prevent or manage diabetes. A healthy diet, weight management, and medication may also be necessary to achieve optimal health outcomes.
| Benefits of Exercise for Diabetes Prevention |
|---|
| Improves insulin sensitivity |
| Reduces blood glucose levels |
| Low-risk of developing type 2 diabetes |
| Improves blood sugar control |
| Reduces the risk of long-term complications |
Case Studies: Real-life Impacts
Explore the correlation between weight loss and diabetes through real-life case studies, shedding light on the profound impacts of losing weight on diabetes prevention and management. Uncover the intricate connection between shedding excess pounds and reducing the risk of developing diabetes.
| Success Stories of Managing Diabetes with Weight Loss | Instances Where Weight Loss Led to Diabetes Complications |
| Many individuals have successfully managed diabetes through weight loss. | However, in some cases, weight loss can trigger diabetes complications. |
| These real-life case studies highlight the positive impact of weight loss. | It is crucial to monitor blood sugar levels closely during weight loss journeys. |
Credit: www.breathewellbeing.in
Preventive Measures And Recommendations
Preventive measures and recommendations play a crucial role in maintaining a healthy weight while minimizing the risk of developing diabetes. Strategies for healthy weight loss include adopting a balanced diet that is rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, while limiting the intake of processed foods and sugary beverages. Regular physical activity is essential for burning calories and improving insulin sensitivity. It is important to monitor and manage blood sugar levels through regular check-ups and medication, if necessary. Weight loss should be gradual and sustainable, aiming for a loss of 1-2 pounds per week. Incorporating stress management techniques and getting enough sleep can also support weight loss efforts. Remember, maintaining a healthy weight can reduce the risk of diabetes and improve overall well-being.
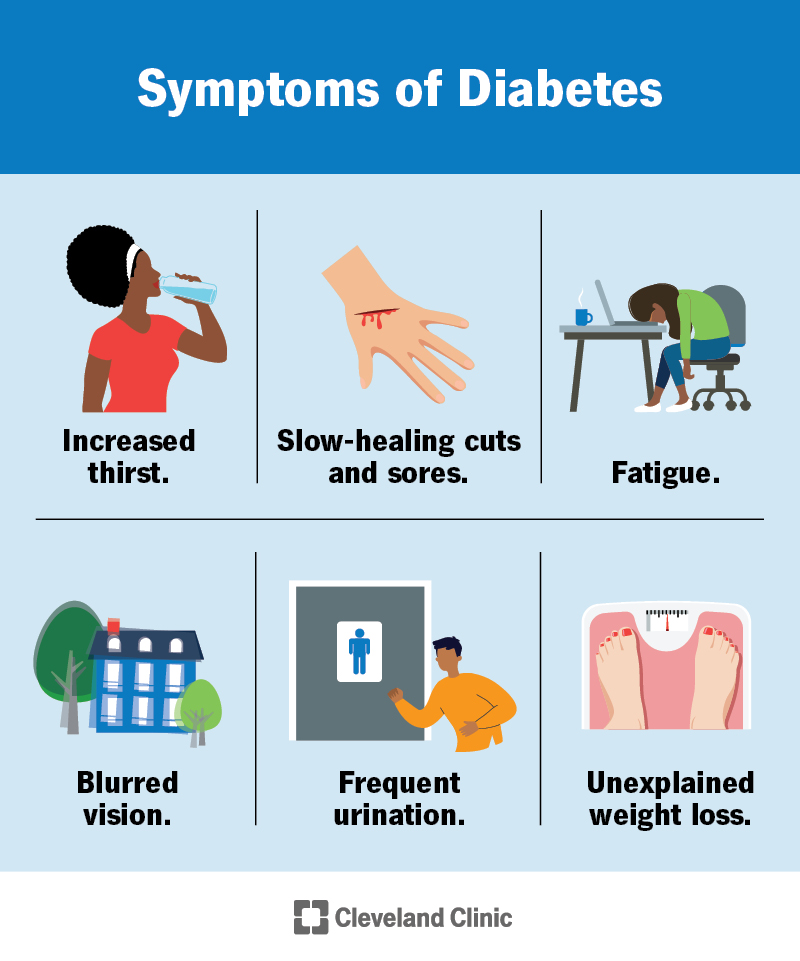
Credit: my.clevelandclinic.org
Conclusion
Weight loss can lead to diabetes due to insulin resistance and hormonal changes. It’s crucial to maintain a healthy weight through balanced diet and regular exercise to prevent diabetes. Understanding the link between weight loss and diabetes is essential for overall health and well-being.
Stay informed and take proactive steps towards a healthier lifestyle.
Your article helped me a lot, is there any more related content? Thanks!